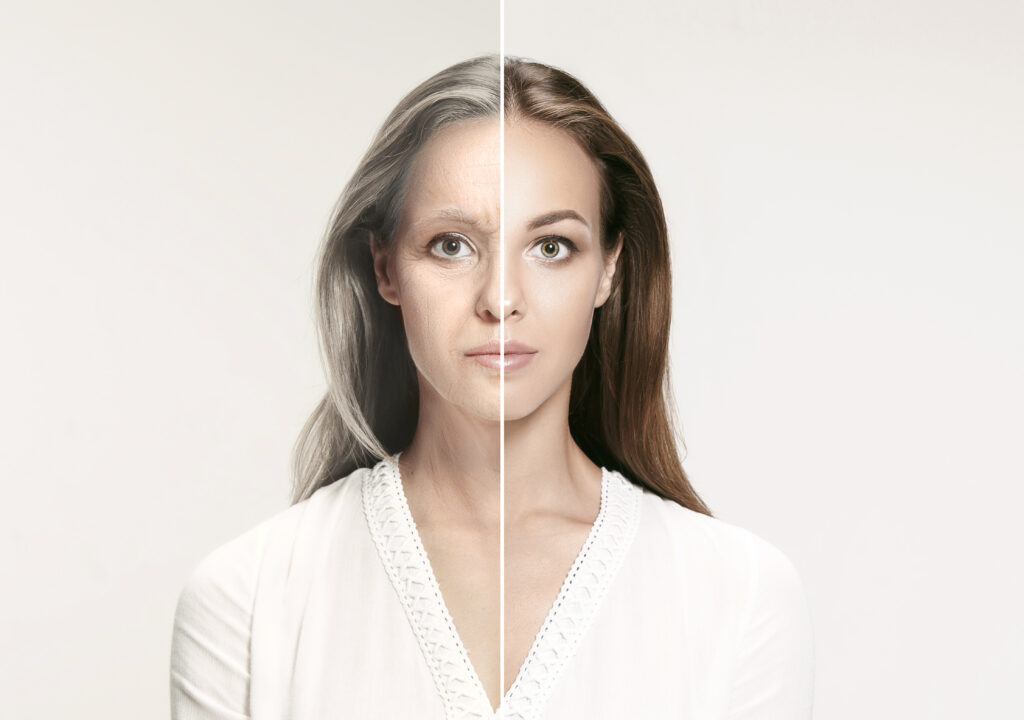
Skin Rejuvenation
Our skin is the largest organ of the body and often the first to show the signs of aging. Exposure to sun, poor diet, alcohol, smoking, lack of sleep, stress can all accelerate the aging of our skin. Genetic factors, changes in metabolism and hormone levels, as well as inflammation and oxidative stress, over time also play major roles. The result is a decline in blood flow and nutrients to the skin and reduced levels of collagen, elastin, and keratin that can show up on our skin as moisture loss, reduced elasticity, skin thinning, lines and wrinkles, irregular pigmentation, and impaired skin repair.
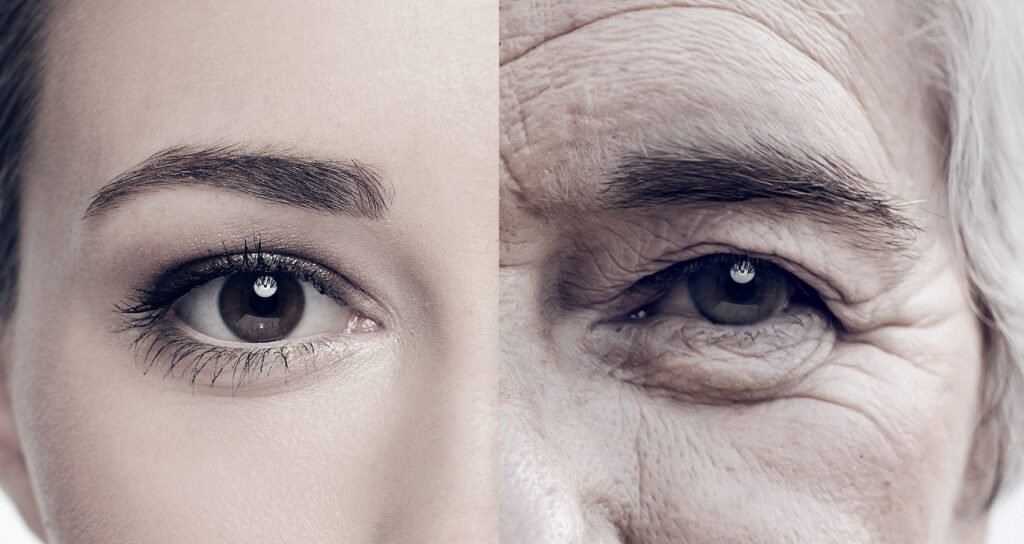

Therapeutic Potential of Muse Cell Exosomes
It is now well established that the therapeutic effects found in MSCs are from the cargo-filled vesicles they release, such as exosomes. These cargos include growth factors, proteins, miRNAs and other components that are taken up by the surrounding cells and used for function and repair.
Within MSC populations, multilineage-differentiating stress enduring (MUSE) cells exist in very small numbers. They are a pluripotent cell that can support the >200 cell types within the body. When the body is under stress or injury, Muse Cells can mobilize and home to the sites of injury. They can also engulf damaged cells and differentiate into the damaged cell type, thus, regenerating tissue.Muse Cells can be expanded in culture to much higher concentrations (30-50% or greater) and the exosomes can be isolated.
Muse Cell Exosomes are unique in that they contain the cargo of pluripotent cells. They are isolated from umbilical cord tissue because it is a young source of MSCs and Muse Cells and provides a more robust cell source without the cellular damage and deterioration found in adult cells. Muse Cell Exosomes offer a cell-free alternative, to reduce the signs of aging and rejuvenate the skin.
Muse Cell Exosomes for Skin Rejuvenation
Skin treatments with Muse cell exosomes can:
- Increase blood flow for better delivery of nutrients
- Reduce inflammation and accelerate skin repair
- Diminish the appearance of lines and wrinkles
- Even out pigmentation and improve texture
- Elevate moisture and firmness for a more youthful appearance
- Reduce recovery downtime
- Improve the health and vitality of skin, boosting confidence
Muse Cell Bio (MCB) is dedicated to advancing knowledge of regenerative medicine and the potential for exosome therapies to have a positive impact on skin rejuvenation. By providing healthcare professionals and patients with critical insights into these innovative treatment options, MCB promotes effective, minimally invasive strategies that enhance quality of life without temporarily disrupting it.
References
Basu J, Ludlow JW. Exosomes for repair, regeneration and rejuvenation. Expert Opin Biol Ther; 2016. pp. 1–18.
Colombo M, et al. Biogenesis, Secretion, and Intercellular Interactions of Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255–289.
Doi H, Kitajima Y, Luo L, Yan C, Tateishi S, Ono Y. et al. Potency of umbilical cord blood- and Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells for scarless wound healing. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18844.
Fisch, S.C., Gimeno, M.L., Phan, J.D. et al. Pluripotent nontumorigenic multilineage differentiating stress enduring cells (Muse cells): a seven-year retrospective. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017,Oct;8:227.
Gaur M., Dobke M., Lunyak V.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue in Clinical Applications for Dermatological Indications and Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:208.
Gong M., Yu B., Wang J., Wang Y., Liu M., Paul C., Millard R.W., Xiao D.S., Ashraf M., Xu M. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:45200–45212.
Kim Y.J., Yoo S.M. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells stimulates rejuvenation of human skin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017;493:1102–1108.
Kinoshita K, Kuno S, Ishimine H, Aoi N, Mineda K, Kato H, Doi K, Kanayama K, Feng J, Mashiko T, et al.. Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived SSEA-3-positive muse cells for treating diabetic skin ulcers. Stem Cell Transl Med 2015; 4:146-55.
Fisch, S.C., Gimeno, M.L., Phan, J.D. et al. Pluripotent nontumorigenic multilineage differentiating stress enduring cells (Muse cells): a seven-year retrospective. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017,Oct;8:227.
Lee H.J., Lee E.G. Efficacy of microneedling plus human stem cell conditioned medium for skin rejuvenation: A randomized, controlled, blinded split-face study. Ann. Dermatol. 2014;26:584–591. doi: 10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.584.
Li Y., Wu Q., Wang Y., Li L., Bu H., Bao J. Senescence of mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017;39:775–782.
Liang X., Zhang L., Wang S., Han Q., Zhao R.C. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J. Cell Sci. 2016;129:2182–2189.

Ready to Transform Patient Care?
Get in touch with our regenerative medicine experts today.
The following videos are publicly hosted on YouTube and are shared solely to provide educational examples of the potential benefits of stem cell therapy. Muse Cell Bio does not endorse, promote, or affiliate with any products, services, or clinics featured or mentioned in these videos.