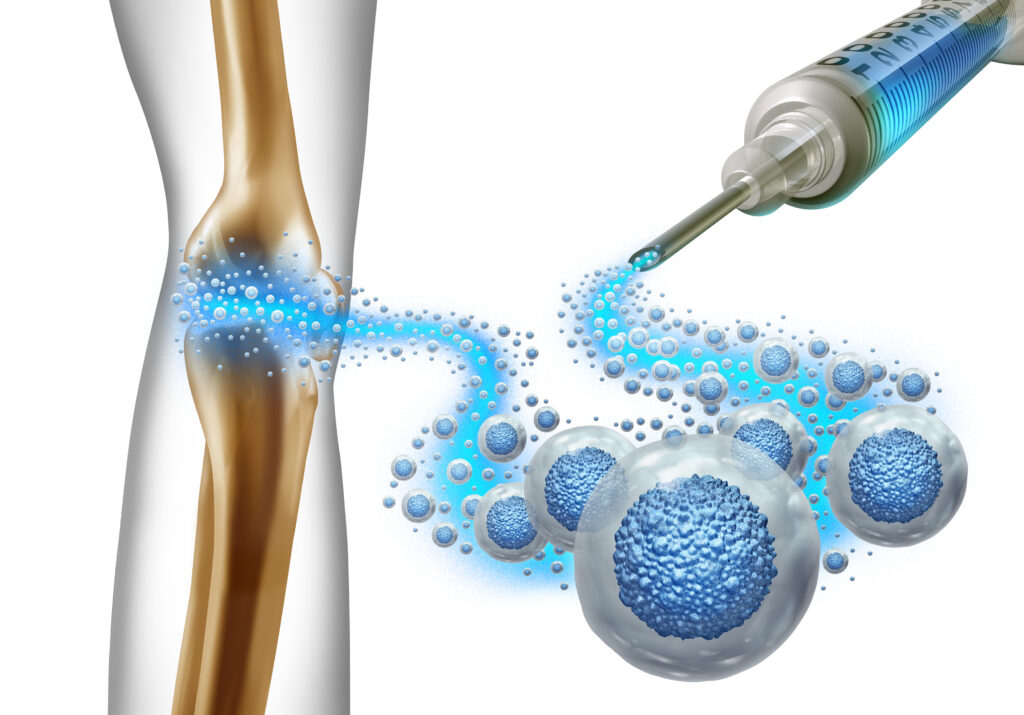
The treatment of osteoarthritis (OA), particularly in the knee joint, presents a significant challenge in modern medicine. Recent research has turned toward innovative therapies involving mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). A noteworthy study led by Kai-Zhen Xiao and colleagues has delved into the efficacy of intra-articular injections of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) for alleviating OA progression.
Historically, many experimental studies on hUC-MSCs have utilized fetal bovine serum (FBS) in their culture systems. However, this method carries ethical concerns and limitations that can hinder clinical applications. The study emphasizes the advantages of serum-free cultures, which not only mitigate the ethical dilemmas associated with FBS but also enhance the potential for broader clinical implementation. By utilizing serum-free conditions, researchers can ensure a more standardized environment for stem cell growth and differentiation, potentially leading to more reliable therapeutic outcomes.
The team behind this research, which includes Gui Liao, Guang-Yu Huang, Yun-Long Huang, and Rong-He Gu, is affiliated with the Department of Orthopedic Surgery and the Graduate School of Guangxi Medical University in Nanning, China. Their collective expertise in orthopedic surgery and regenerative medicine has been crucial in exploring the potential of hUC-MSCs as a viable treatment option for knee osteoarthritis.
The implications of this research are profound. With the increasing prevalence of OA, a condition that significantly affects the quality of life, the search for effective treatments is more critical than ever. The findings from this study could pave the way for using hUC-MSCs as a therapeutic alternative, providing hope for millions suffering from this debilitating condition.
As the field of regenerative medicine continues to grow, studies like this one are essential in moving towards more effective, ethical, and clinically applicable therapies. The future of OA treatment may well lie in the innovative application of stem cell technology, and this research marks a significant step in that direction.